Blood in Urine: Could It Be Bladder Cancer?
Oct 30, 2024
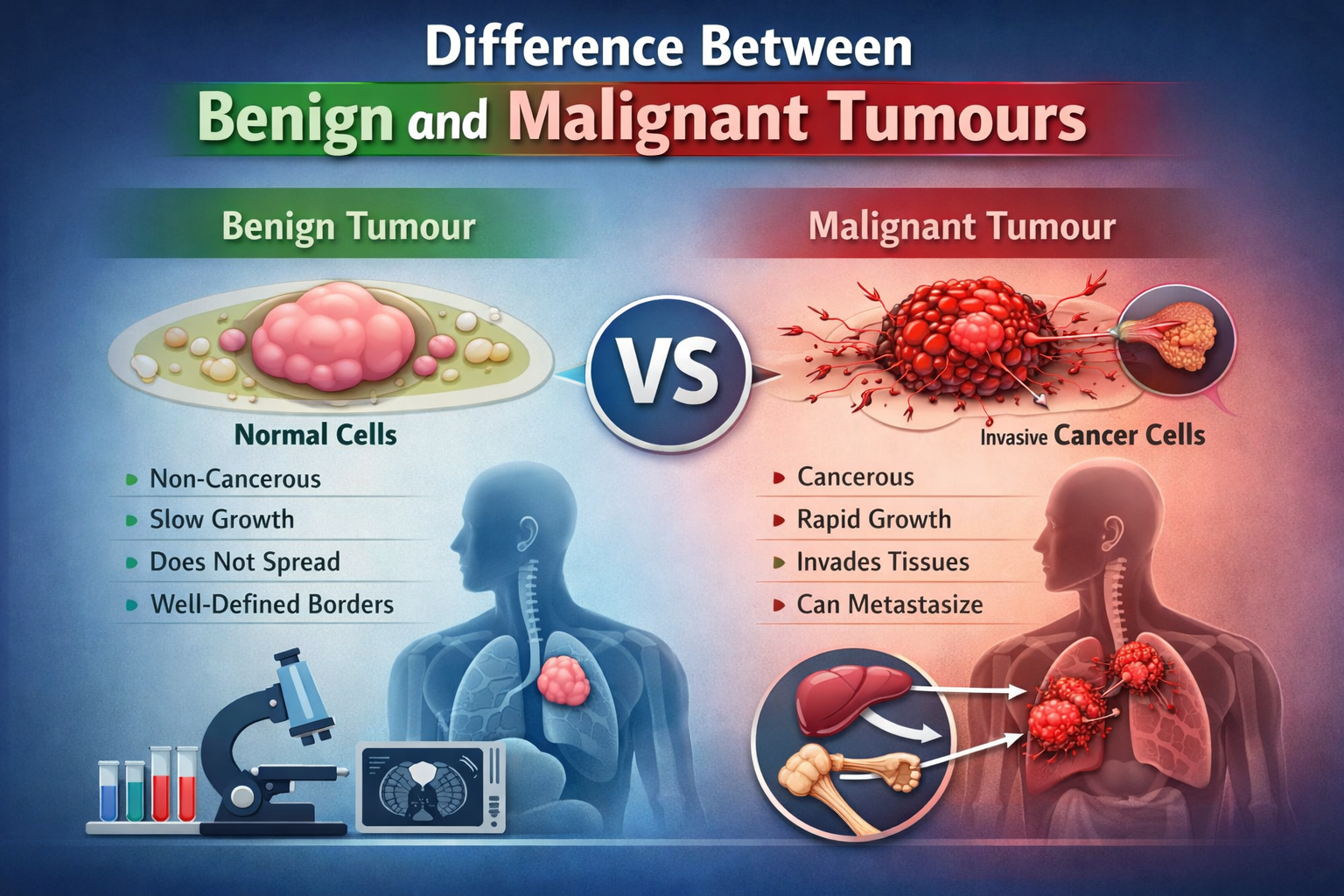
Hearing the word tumour can be alarming, but not all tumours are cancerous. Tumours are broadly classified into benign and malignant, and understanding the difference between the two is crucial for timely diagnosis, correct treatment, and peace of mind. This blog explains the key differences between benign and malignant tumours in a clear, patient-friendly manner, while also highlighting the importance of expert oncology care under Dr Sumant Gupta, widely regarded as the best oncologist in Faridabad.
A tumour is an abnormal growth of cells that forms when cells divide uncontrollably. Tumours can develop in almost any part of the body, including organs, bones, muscles, and blood-forming tissues.
Based on their behaviour, tumours are classified into:
Benign tumours (non-cancerous)
Malignant tumours (cancerous)
A benign tumour is a non-cancerous growth that usually grows slowly and does not spread to other parts of the body.
Grow at a slow pace
Remain localised to one area
Do not invade nearby tissues
Do not spread (metastasise) to distant organs
Usually have well-defined borders
Often resemble normal cells under a microscope
Lipoma (fat tissue tumour)
Fibroma (fibrous tissue tumour)
Adenoma (glandular tissue tumour)
Benign breast lumps
Uterine fibroids
Most benign tumours are not life-threatening. However, they may still require treatment if they:
Press on vital organs or nerves
Cause pain or discomfort
Interfere with normal body functions
Have a risk of becoming malignant (rare but possible in some cases)
A malignant tumour is cancerous and can grow aggressively. These tumours have the ability to invade surrounding tissues and spread to distant organs through the blood or lymphatic system.
Grow rapidly or unpredictably
Invade surrounding healthy tissues
Can spread to other parts of the body (metastasis)
Cells look abnormal under a microscope
Can recur even after treatment
Carcinomas (lung, breast, colon cancer)
Sarcomas (bone, muscle, connective tissue cancers)
Leukemia (blood cancer)
Lymphoma (lymphatic system cancer)
Myeloma (bone marrow cancer)
Malignant tumours require immediate medical attention and specialised cancer treatment.
| Feature | Benign Tumour | Malignant Tumour |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Non-cancerous | Cancerous |
| Growth rate | Slow | Fast or uncontrolled |
| Spread | Does not spread | Can spread to other organs |
| Invasion | No invasion of nearby tissues | Invades surrounding tissues |
| Cell appearance | Normal-looking cells | Abnormal, irregular cells |
| Recurrence | Rare | Common if not treated properly |
| Risk to life | Usually low | Potentially life-threatening |
Painless lump or swelling
Mild discomfort due to pressure
Often discovered incidentally
Persistent or increasing pain
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue
Fever or night sweats
Bleeding or discharge
Change in bowel or bladder habits
Persistent cough or difficulty breathing
If symptoms persist or worsen, it is essential to consult an oncologist.
Accurate diagnosis is critical to distinguish between benign and malignant tumours. An experienced oncologist like Dr Sumant Gupta follows a structured diagnostic approach that may include:
Physical examination
Imaging tests (X-ray, CT scan, MRI, PET-CT)
Blood tests and tumour markers
Biopsy (gold standard for diagnosis)
Genetic and molecular testing (when required)
Early and precise diagnosis plays a vital role in successful treatment outcomes.
Observation and regular monitoring
Surgical removal if symptomatic
Minimal follow-up after removal
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy
Bone marrow transplant (in selected cases)
Treatment plans are customised based on cancer type, stage, patient health, and response to therapy.
Early identification of a malignant tumour:
Improves survival rates
Allows less aggressive treatment
Reduces complications
Enhances quality of life
Even benign tumours should not be ignored, as timely evaluation ensures safety and reassurance.
Managing tumours requires specialised knowledge, advanced diagnostic tools, and a multidisciplinary approach. Dr Sumant Gupta, the best oncologist in Faridabad, is known for his expertise in:
Medical oncology
Hematology
Bone marrow transplant (BMT)
Comprehensive cancer care
With a patient-centric approach, he focuses not only on treatment but also on emotional support, counselling, and long-term follow-up.
You should seek oncology consultation if you notice:
A new or growing lump
Persistent pain or swelling
Unexplained weight loss
Long-lasting fatigue
Abnormal bleeding
Symptoms that do not improve with routine treatment
Early consultation can make a significant difference.
Understanding the difference between benign and malignant tumours empowers patients to take informed decisions about their health. While benign tumours are usually harmless, malignant tumours are serious and require immediate expert care.
If you or your loved ones are facing concerns related to tumours or cancer, consulting an experienced specialist like Dr Sumant Gupta, the best oncologist in Faridabad, ensures accurate diagnosis, advanced treatment, and compassionate care at every step of the journey.
Early action saves lives. Never ignore the signs.
Oct 30, 2024
Oct 30, 2024
Oct 30, 2024